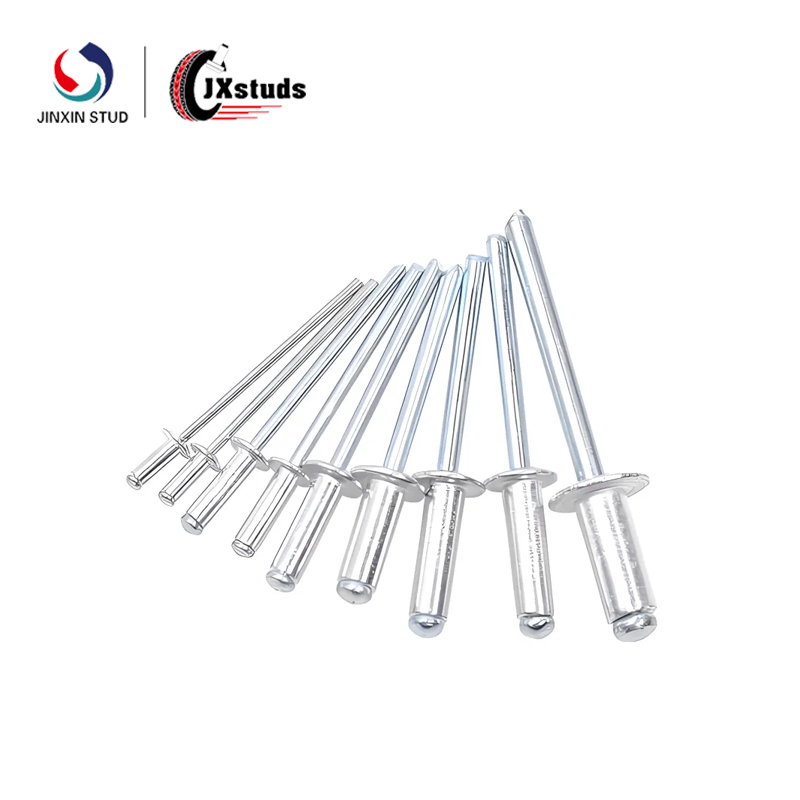
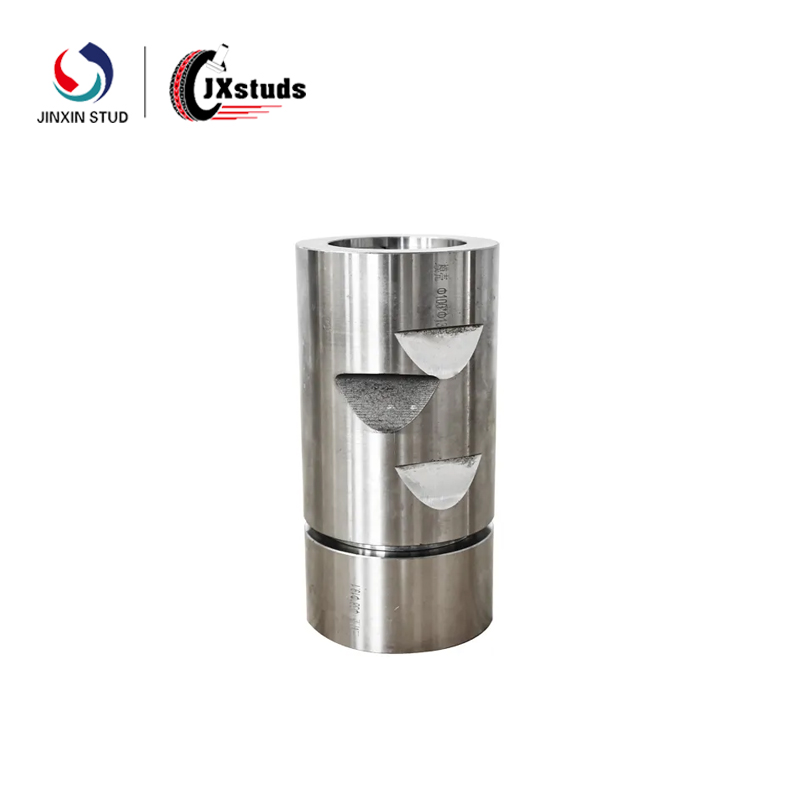
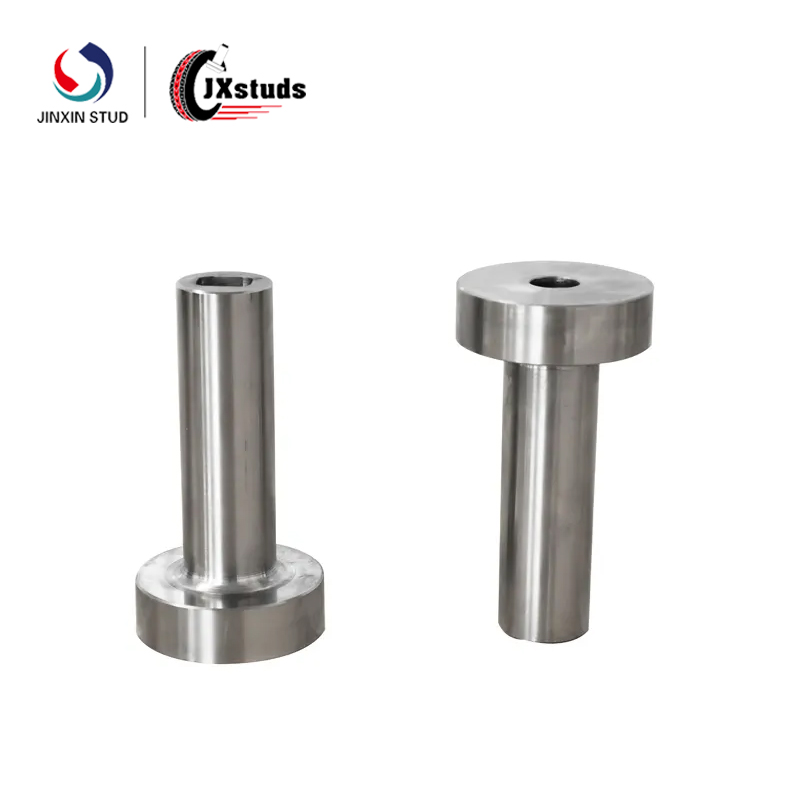
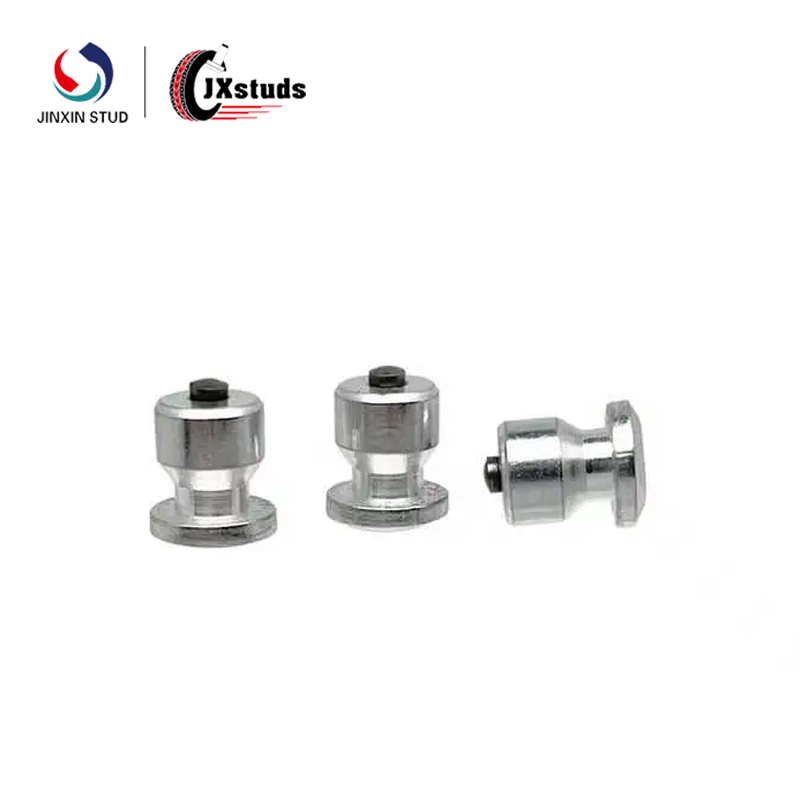
1. Definition of Cold Heading Mold: A cold heading mold is a tool used to shape metal in a cold state, usually consisting of two and a half molds, upper and lower, and a set of mold cores. Through the clamping action of the upper and lower molds and the pushing of the mold core, the metal material undergoes plastic deformation in the mold, ultimately forming shapes such as threads and grooves.
2. Classification of cold heading molds: According to different usage purposes and process requirements, cold heading molds are mainly divided into three types: thread cold heading molds, head forming cold heading molds, and special cold heading molds.
(1) Thread cold heading mold: mainly used for producing threaded products, including internal threads, external threads, and special threads.
(2) Head forming cold heading mold: used to produce products with heads, such as bolts, nuts, etc.
(3) Special cold heading mold: Design and manufacture cold heading molds with special shapes according to specific product requirements
Main components and material selection of cold heading molds
1. Main components of cold heading molds: Cold heading molds mainly include upper and lower molds, mold cores, and mold seats. The upper and lower molds are used to clamp metal materials and complete the forming process through the clamping action, while the mold core is used to support and form the internal structure of the material.
2. Material selection for cold heading molds: The materials for cold heading molds need to have high hardness, high strength, good wear resistance, and fatigue performance. Common cold heading die materials include alloy steel
High speed steel, hard alloys, etc.
The manufacturing process of cold heading molds
1. Design of Cold Heading Mold: The design of cold heading mold needs to meet the technical and process requirements of the product, including the structural shape, dimensional accuracy, surface smoothness, etc. of the product. When designing, it is necessary to consider factors such as the strength, stiffness, and temperature changes of the mold.
2. Processing technology of cold heading molds: The processing technology of cold heading molds includes rough machining, heat treatment, precision machining, assembly, and debugging. Among them, heat treatment is crucial for improving the hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue performance of the mold.
The use and maintenance of cold heading molds
1. Use of cold heading molds: When using cold heading molds, it is necessary to select appropriate process parameters based on product requirements and mold characteristics, and strictly control the quality and dimensional accuracy of the forming.
2. Maintenance of cold heading molds: Cold heading molds require regular maintenance and upkeep during use, including cleaning and lubrication of the mold surface, repair of wear, and timely replacement of damaged parts.
Hard alloy molds mainly include the following categories
1. Wire drawing molds. This type of mold accounts for a large proportion in hard alloy molds, with main grades including YG8, YG6, YG3, etc
2. Cold heading die and cold stamping die. The main grades include YC20C, YG20, YG15, etc
3. Integral mold. The main grades of this type include CT35, YJT30, and MO15.
4. Non magnetic alloy molds. Mainly used for the production of magnetic materials。Grade such as YSN series YSN (including 20, 25, 30, 35, 40) and steel structure non-magnetic mold grade -TMF
5. Hot work molds. There is currently no standard brand for this type of mold, but market demand is increasing
general impact-resistant forging die
6. punching and shearing molds, as well as in large impact forming and stamping molds
stamping dies such as progressive dies.
7. In addition, there are some special types of molds, such as hexagonal molds, spiral molds and other non-standard molds etc.
Product Paramenters
Grade | ISO | Density | TRS | Harness | Applications |
YG11C | K40 | 14.35 | 2200 | 87.6 | Forming or stamping dies for metal powders and nonmetal powders. |
YG15 | K40 | 14.0 | 2300 | 86.5 | For fabricating drawing dies of steel tubes and rods under high compressibility ratio;punchingstampingforging tools under large stress. |
YG15C | K40 | 14.0 | 2500 | 85 | |
YG18C | K40 | 13.7 | 2700 | 84.5 | Impact resistance forging dies,hot-press forging dies and rollers. |
YG20 | K40 | 13.5 | 2400 | 4 | For various dies made by cold forging,cold stamping and hot forging. |
YG20C | K40 | 13.4 | 2600 | 81-82 | Dies for wear resistant or impact resistant application |
YM3 | K05 | 15.1 | 1400 | 92 | suitable for fnishing of cast iron and nonferrous metal |
YM6X | K10 | 14.95 | 1800 | 91.5 | the finishing & semi-finishing of cast iron and nonferrous metals and also for the machining of manganese steel and hardening steel |
YM6 | K15 | 14.95 | 1900 | 90.5 | suiable for the roughing of cast iron and light alloys and also for themilling of cast iron and low-alloy steel |
YM8 | K20 | 14.8 | 2200 | 89.5 | |
YW1 | M10 | 13.1 | 1600 | 91.6 | suitable for fnishing and semi-finishing of stainless steel and conventionalalloy steel |
YW2 | M20 | 13 | 1800 | 90.6 | the grade can be used for the semi-finishing of stainless steel andlow-alloy steel and it is mainly used for the machining of railway |
YT15 | P10 | 11.4 | 1600 | 91.5 | suitable for the fnishing and semi-finishing for steel and cast steel witha moderate feed rate and rather high cutting speed |
YT14 | P20 | 11.6 | 1700 | 90.8 | suitable for the fnishing and semi-finishing of steel and cast steel |
YT5 | P30 | 12.9 | 2200 | 90.5 | suitable for the heavy duty rough turning of and cast steel with a bigfeed rate at a medium and low speed under unfavorable workingconditions. |