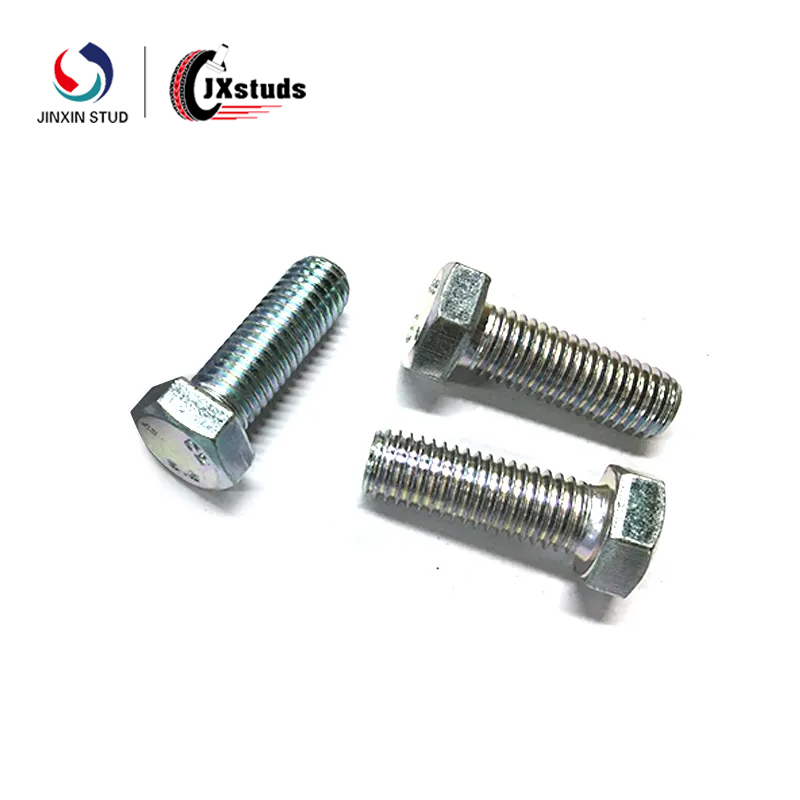
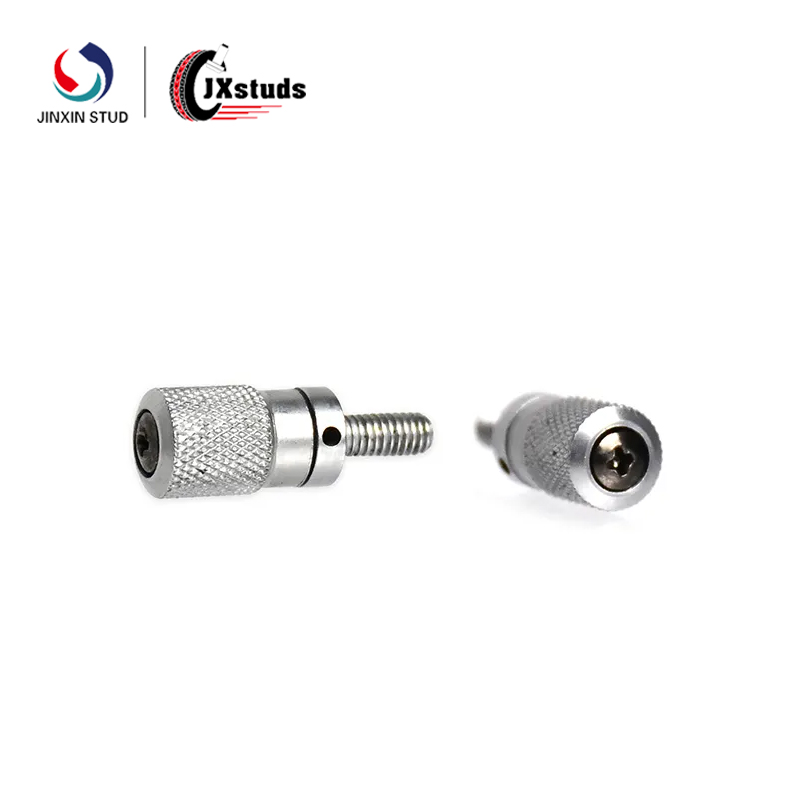
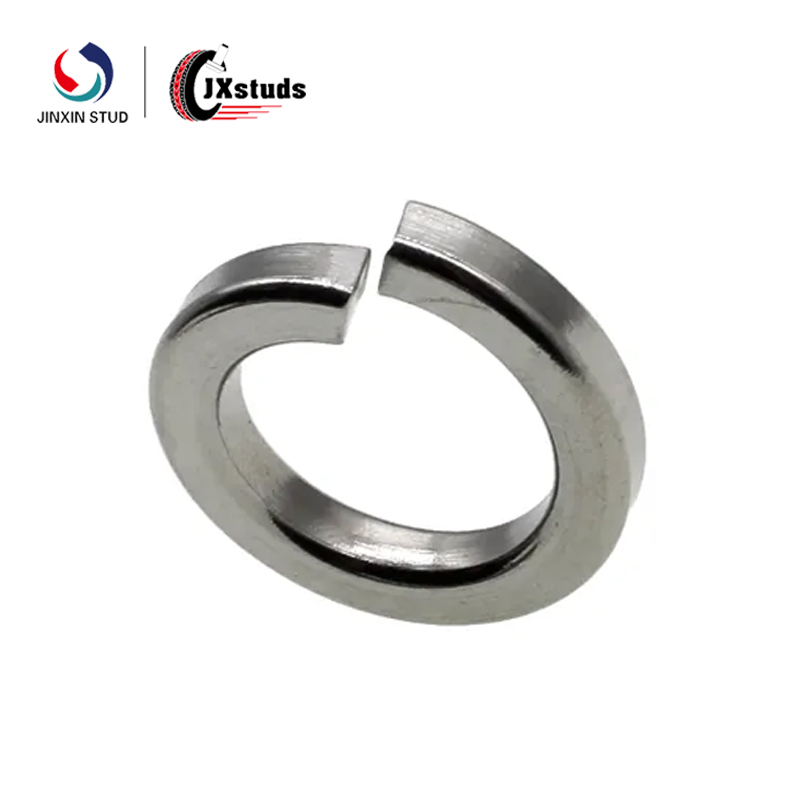
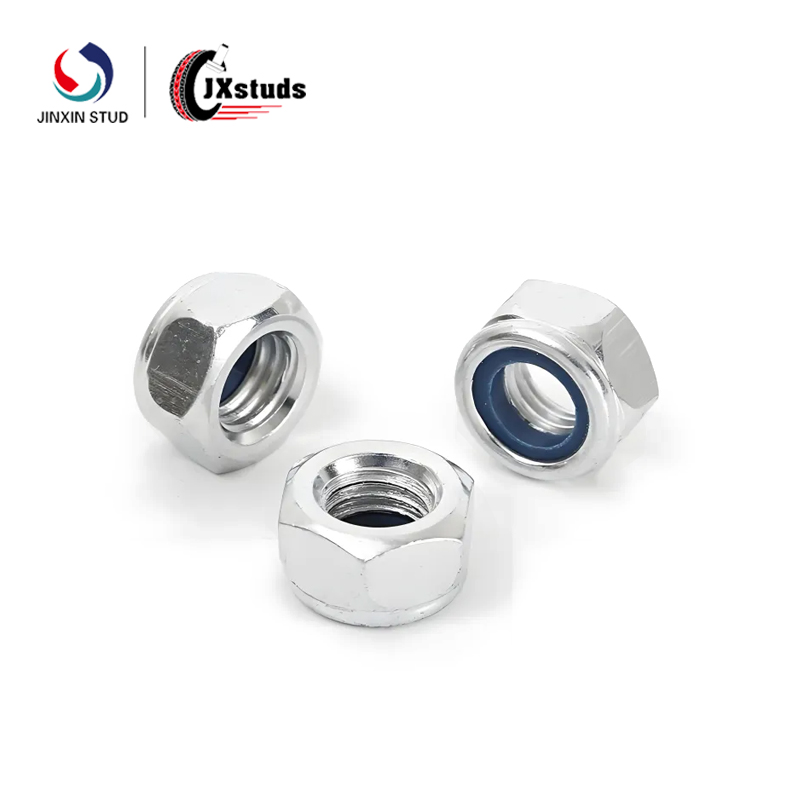
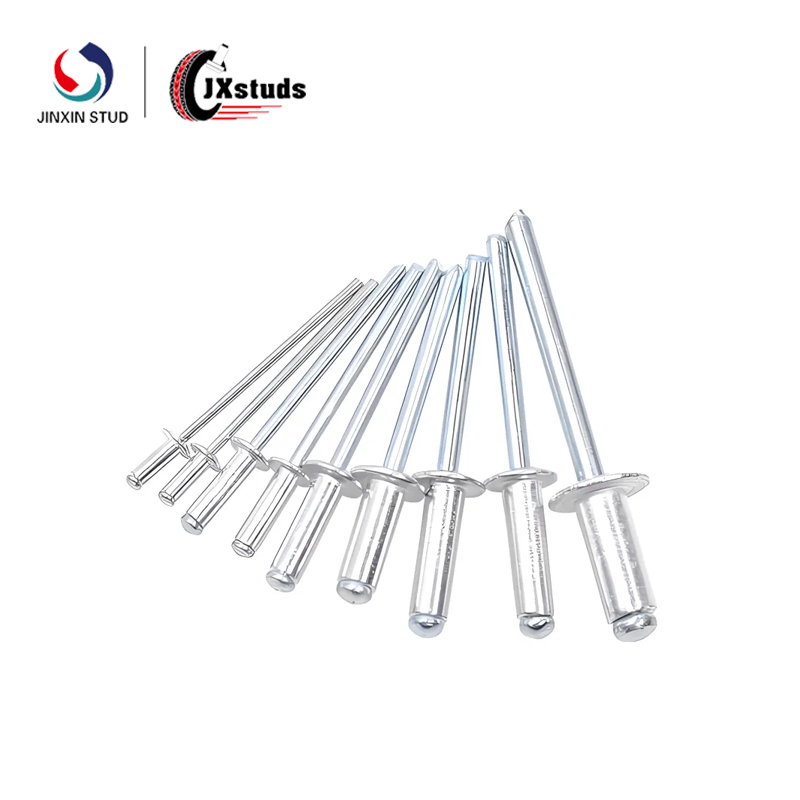
Cold heading is a pressure processing method that utilizes the plasticity of the metal at room temperature and uses a cold heading machine to form the metal billet by upsetting (often locally). For the production of fasteners (such as bolts, nuts, etc.), the cold heading process can efficiently mass produce parts with complex shapes and high precision.

Cold heading molds are used to produce plastic deformation of the blanks in the mold cavities to obtain fasteners of the required shape and size. The process usually consists of several steps such as positioning, clamping, upsetting and demolding of the blank.
The manufacturing of cold heading molds requires mold design according to the specific shape of the fastener, dimensional accuracy requirements, batch size and other factors. For example, for cold heading molds for high strength bolts, it is necessary to consider the bearing capacity and abrasion resistance of the mold, because in the upsetting process, the mold has to withstand high pressure.
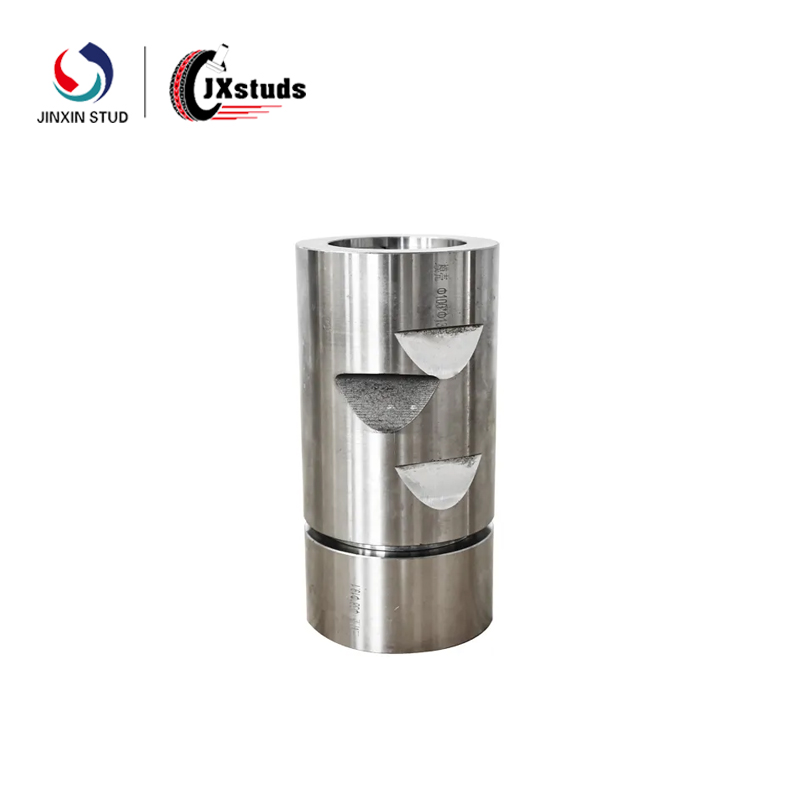
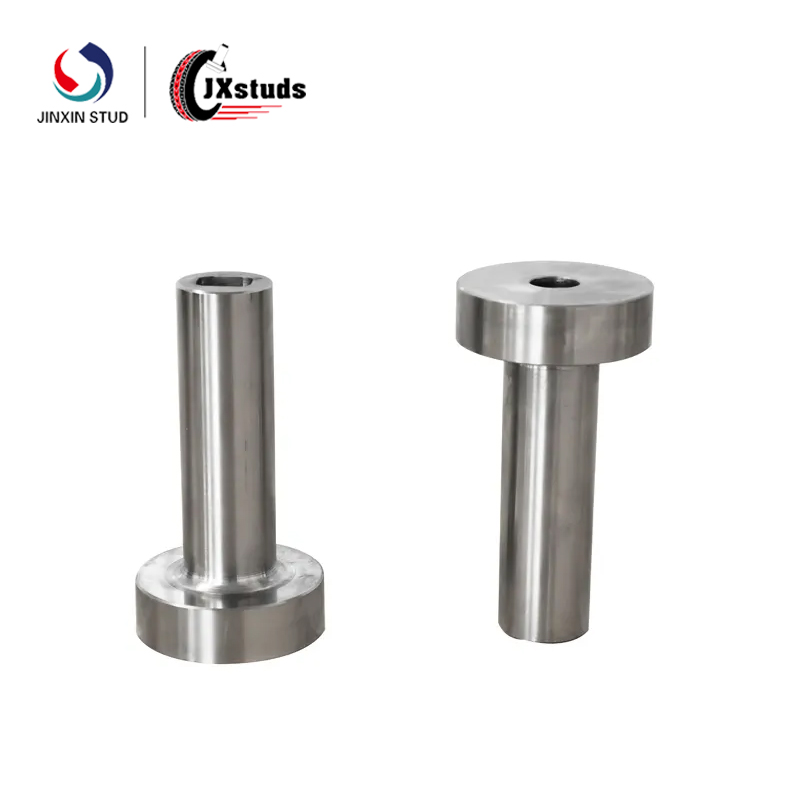
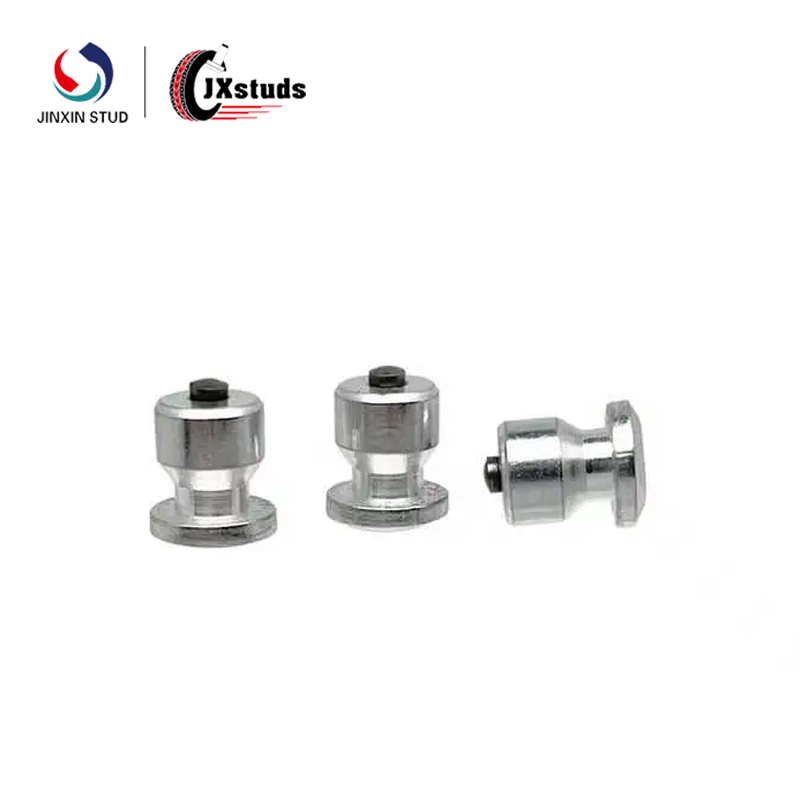
Cold heading molds generally include punches, concave molds, ejector devices and other major components. When designing, the shape, size and mutual relationship of each part should be reasonably determined. Taking the nut cold heading mold as an example, the shape of the cavity of the concave die should be precisely matched with the shape of the nut, and the uniformity of the metal flow should be taken into consideration to ensure the dimensional accuracy of each part of the nut.
According to the working conditions and performance requirements of the mold, choose the appropriate mold material. For the cold heading mold parts that are subject to high impact load and high friction, such as punches, hard alloy or high performance mold steel (such as Cr12MoV, etc.) is often used. These materials have high hardness, high strength and good wear resistance.