Screws are usually screwed directly into the object itself, relying on their own external threads and internally threaded holes (or tapped directly into the material) for connection, with self-locking ability.
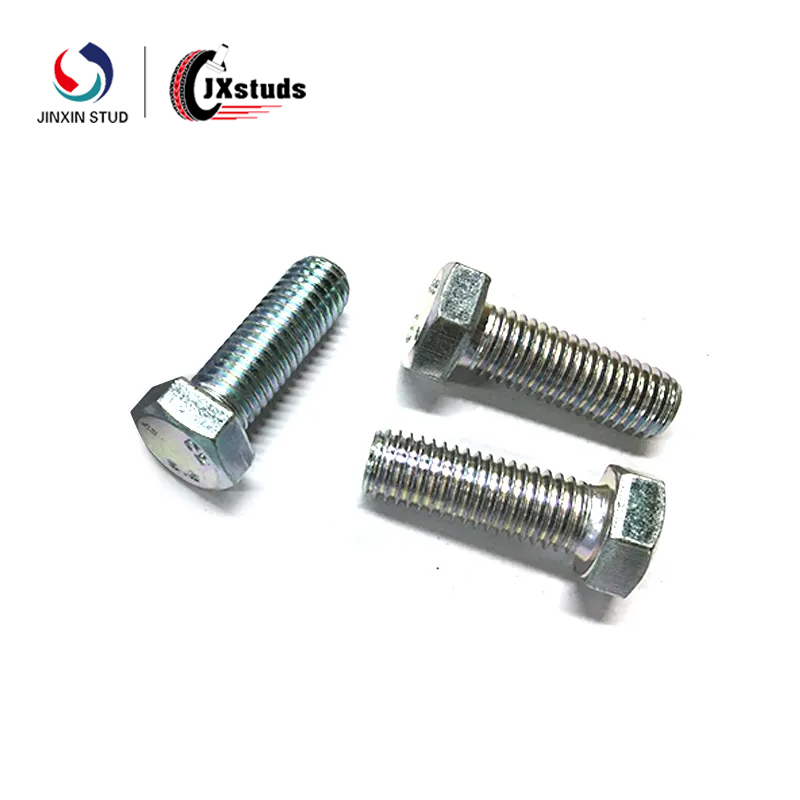
Bolts are usually used in conjunction with nuts, and need to be threaded through the hole of the workpiece and then locked by the nut, suitable for occasions that require higher connection strength.
Screws and bolts identification method
1. Whether a nut is required
Bolts are usually used in conjunction with nuts and are suitable for mechanical connections.
Screws are mostly self-locking connections that do not require a nut, and are suitable for plastics, wood, and metal shells.
2. Head type
Bolts are commonly hexagonal heads, which are easy to be fixed with a wrench.
Screws have a variety of head types, such as Phillips head, hexagonal head, round head, countersunk head, etc., which is easy to install with a screwdriver or hexagonal wrench.
3. Thread pattern
Bolts are mostly coarse threaded or partially threaded, suitable for high-strength connections.
Screws are usually fully threaded and have self-tapping and self-locking characteristics.

4. Connection method
Bolt connection requires piercing, nut locking, solid connection but slightly cumbersome to disassemble.
Screw connection can be directly tapped into the workpiece, without additional parts, easy to install.
Screws and bolts of different types also have different application scenarios, such as in home furniture assembly, screws can easily connect different plates together to achieve rapid assembly and disassembly of furniture. In automobile manufacturing, the engine, chassis and other key parts of the connection is also inseparable from the bolt, to ensure that the vehicle at high speeds and complex road conditions between the parts of the connection is solid and reliable.