Product Introduction of Mechanical Screws
1. Overview
Mechanical screws are essential fastening components in the mechanical industry. They play a crucial role in assembling various mechanical structures, providing reliable connections between different parts.
2. Types of Mechanical Screws
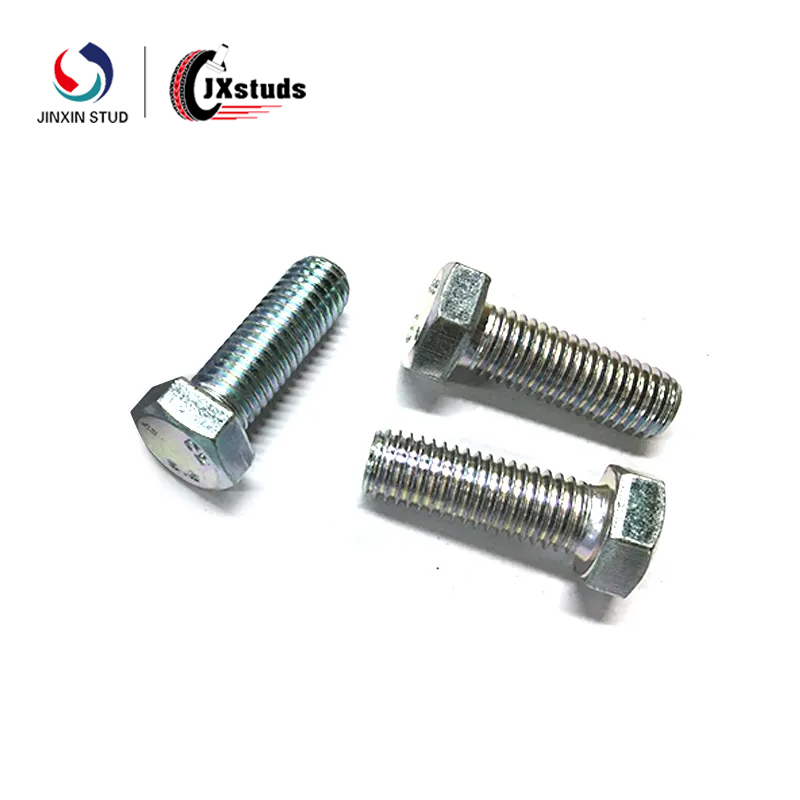
Slotted Screws: These are traditional mechanical screws with a single slot on the head. They are simple in design and can be tightened or loosened using a flat - bladed screwdriver. Commonly used in light - duty applications and some household items.
Phillips Screws: Phillips screws feature a cross - shaped recess on the head. This design allows for better torque transfer during installation compared to slotted screws. They are widely used in a variety of mechanical products, from small electronic devices to larger machinery components.
Hex Socket Screws: The head of these screws has a hexagonal socket. They offer high - precision tightening and are suitable for applications where a greater amount of torque needs to be applied. Hex socket screws are often used in automotive engines, industrial equipment, and precision machinery.
Torx Screws: Torx screws have a unique star - shaped recess in the head. This design provides enhanced torque transfer and reduces the risk of cam - out (screwdriver slipping out of the screw head). They are commonly found in high - performance mechanical systems and some consumer electronics.
3. Material Selection
Carbon Steel: Mechanical screws made from carbon steel are cost - effective and have good strength. They are suitable for general - purpose applications where corrosion resistance is not a major concern. However, carbon steel screws may require additional surface treatments such as plating in some environments.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel screws are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in environments with moisture, chemicals, or high humidity. They are commonly used in food processing equipment, marine applications, and outdoor machinery.
Alloy Steel: Alloy steel screws are designed to provide high strength and durability. They can withstand heavy loads and are often used in high - stress applications such as in the aerospace industry, heavy - duty machinery, and high - performance automotive components.
4. Thread Design
Coarse Thread: Coarse - thread mechanical screws have a relatively large pitch between threads. They are easy to install and provide strong fastening in applications where high precision is not required. Coarse - thread screws are often used in woodworking and some general - purpose mechanical assemblies.
Fine Thread: Fine - thread screws have a smaller pitch, which allows for more precise adjustment and higher holding power. They are suitable for applications where a tight and secure connection is needed, such as in precision mechanical systems and some high - load - bearing structures.
5. Size and Specification
Length: Mechanical screws are available in a wide range of lengths to accommodate different connection requirements. The length is measured from the top of the screw head to the end of the thread, and it is crucial to select the appropriate length to ensure proper engagement with the mating parts.
Diameter: The diameter of the screw, including the shank and the thread diameter, varies according to the specific application. Choosing the correct diameter ensures the screw can withstand the expected loads and fit snugly within the connection holes.
Thread Standard: Mechanical screws follow various thread standards such as metric threads, UNC (Unified National Coarse) threads, and UNF (Unified National Fine) threads. These standards ensure compatibility and interchangeability within the mechanical systems.